Introduction
ZOO Calrissian Runner provides a bridge between the ZOO Project and Calrissian using pycalrissian.
The goal is to ease the development of runners that implement a business logic for the EOEPCA ADES Zoo implementation.
A runner provides an execution engine for Zoo. This repository and documentation provides a runner for Kubernetes using Calrissian.
Below an overview of the building block
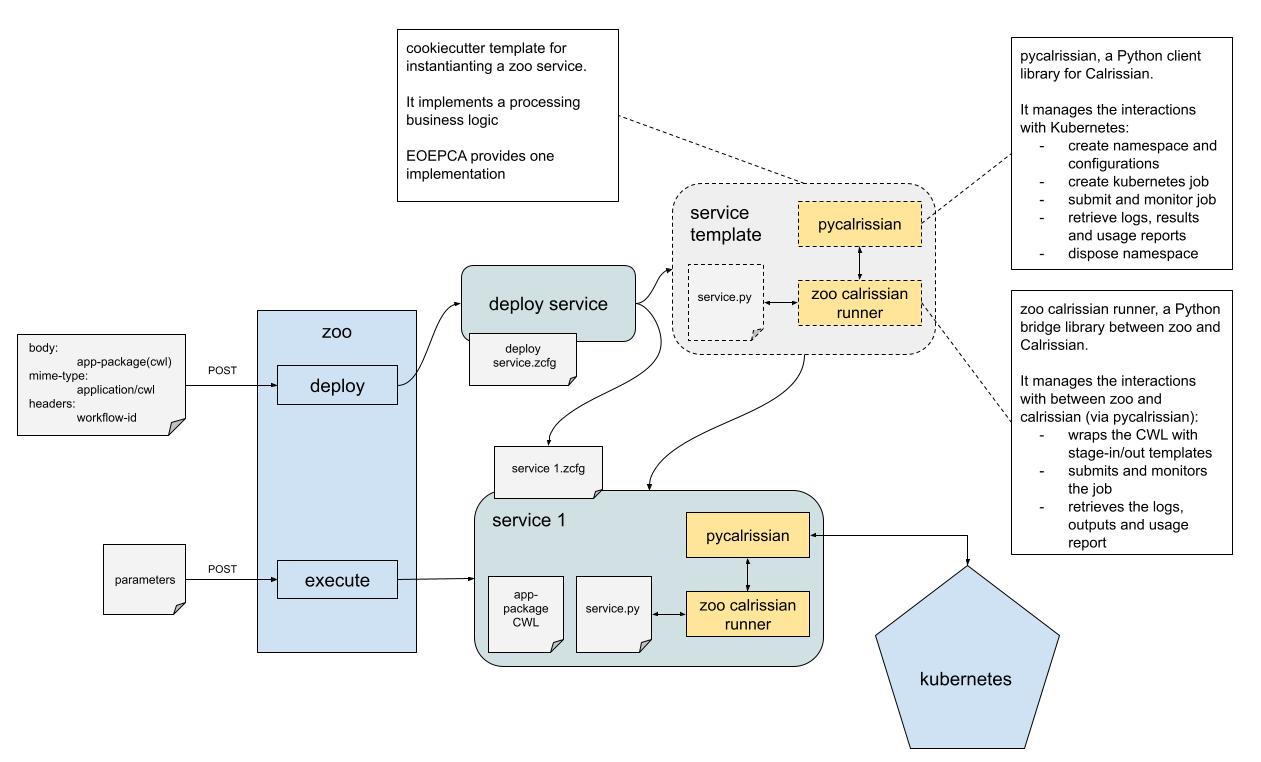
Service deployment
When a service is deployed, the ADES instantiates a cookiecutter processing service template.
The scaffolded service folder contains a service.py Python file that executes the Application Package.
The service.py must implement a function with the signature:
def {{cookiecutter.workflow_id | replace("-", "_") }}(conf, inputs, outputs):
And return zoo.SERVICE_SUCCEEDED if the execution is a success or zoo.SERVICE_FAILED if failed.
It must also implement an ExecutionHandler.
The ExecutionHandler is a abstract class defined as follows:
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
class ExecutionHandler(ABC):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
self.__dict__.update(kwargs)
self.job_id = None
def set_job_id(self, job_id):
self.job_id = job_id
@abstractmethod
def pre_execution_hook(self):
pass
@abstractmethod
def post_execution_hook(self):
pass
@abstractmethod
def get_secrets(self):
pass
@abstractmethod
def get_pod_env_vars(self):
pass
@abstractmethod
def get_pod_node_selector(self):
pass
@abstractmethod
def handle_outputs(self, execution_log, output, usage_report, tool_logs=None):
pass
@abstractmethod
def get_additional_parameters(self):
pass
Service execution
The service execution follows the ZooCalrissianRunner execution defined in its execute method.
What EOEPCA provides
EOEPCA provides:
- a example of a Zoo service template in the https://github.com/EOEPCA/proc-service-template software repository
- an implementation including the interaction with the Workspace API and the Catalog in the https://github.com/EOEPCA/eoepca-proc-service-template software repository
Other service template can of course be implemented with different business logics and interfacing with other systems or APIs.